Stage 13
 Stage
13 is short, lasting for about 1 hour (9:20-10:20 h). It is initiated
by the completion of germ band shortening, when the prospective anal pads
occupy the posterior egg pole and ends with the beginning of head involution.
Stage
13 is short, lasting for about 1 hour (9:20-10:20 h). It is initiated
by the completion of germ band shortening, when the prospective anal pads
occupy the posterior egg pole and ends with the beginning of head involution.
 The
clypeolabrum becomes thinner and starts to retract; retraction of the
clypeolabrum gives rise ventrally to a conspicuous triangular gap, at
the anterior egg pole. At the same time the labium moves to the ventral
midline, becoming manifest due to the displacement of the opening of the
salivary gland duct. The so-called dorsal fold (dorsal ridge) will appear
in the anterior dorsal gap. Posterior and anterior midgut primordia, which
have fused in stage
12, form a thin epithelium on either side of the yolk sac.
The
clypeolabrum becomes thinner and starts to retract; retraction of the
clypeolabrum gives rise ventrally to a conspicuous triangular gap, at
the anterior egg pole. At the same time the labium moves to the ventral
midline, becoming manifest due to the displacement of the opening of the
salivary gland duct. The so-called dorsal fold (dorsal ridge) will appear
in the anterior dorsal gap. Posterior and anterior midgut primordia, which
have fused in stage
12, form a thin epithelium on either side of the yolk sac.
Cells of the midgut epithelia expand over the yolk sac
to make contact along the ventral and dorsal midline and eventually fuse.
This process takes quite a long time to be complete, extending into stages
14 and 15.
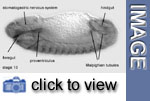 The
hindgut opens in the anus. At the beginning of stage 13 the hindgut consists
of an empty longitudinal tube, contiguous with the midgut epithelia. Four
thin Malpighian tubules can be distinguished sprouting from its ventral
side.
The
hindgut opens in the anus. At the beginning of stage 13 the hindgut consists
of an empty longitudinal tube, contiguous with the midgut epithelia. Four
thin Malpighian tubules can be distinguished sprouting from its ventral
side.
Three different regions can be distinguished in the foregut, the pharynx, consisting of the pharyngeal roof and hypopharyngeal lobes, the prospective esophagus and the proventriculus. The three invaginations of the stomatogastric nervous system have disappeared, their cells becoming distributed within the clypeolabrum.
The two developing salivary gland lobes join to form
a common midsagittal duct behind the hypopharyngeal lobes at the beginning
of stage 13; the salivary gland duct will be displaced towards the foregut
as the labial appendages move frontalward during mouth involution. The
salivary glands diverge bilaterally from the common duct, extending between
the epidermis and the ventral cord beneath the midgut.
The epidermis of the procephalic lobe and clypeolabrum ends at the interface
with the amnioserosa, contiguous with the dorsal ridge. The dorsal ridge
during stage 13 extends dorsalwards to fuse eventually across the dorsal
midline with ist complement on the other side. After germ band shortening,
the dorsal surface of the embryo is formed by the amnioserosa, which is
characterized by extremely thin and flat cells that abut the dorsal epidermis.
However, during stage 13 the epidermal layer starts to extend dorsally
over the amnioserosa towards the dorsal midline, ultimately leading to
dorsal closure of the embryo.
The developing central nervous system consists of the
well differentiated ventral cord and the supraoesophageal ganglion. Neuromere
organization is clearly distinguishable within both the ventral nerve
cord and the suboesophageal ganglion. Ventral cord and suboesophageal
ganglion extend from the tip of the hypopharyngeal lobe to the region
immediately ventral to the anus, and will maintain this length until stage
15, when ventral cord condensation sets in. The primordia of the optic
lobes have become integrated into the posteroventral region of the supraoesophageal
ganglion, although their cells can still be distinguished cytologically.
Fibre connectives and commissures linking the different neuromeres are
formed. Progenitors of sensory cells, including the primordia of the antenno-maxillary
complex, appear in the epidermis of maxilla, mandible and procephalic
lobe. At the end of stage 13 muscle cells become apparent, inserting at
incipient apodemes of the lateral epidermis.
![]()
Media list
Genes discussed
|
Gene
|
Gene product - Domains
|
Function
|
Links
|
|
crumbs (crb)
|
transmembrane -EGF repeats - laminin A homolog
|
involved in epithelial polarity, expressed in the apical
membrane of ectodermal cells
|