Gap genes
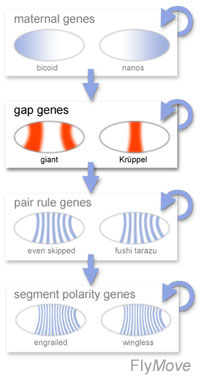 The
gap genes subdivide the embryo into broad domains. Their (zygotic) expression
is regulated by maternal gene products, like Bicoid. In addition, gap
genes regulate each other, leading to a refinement of their expression
patterns.
The
gap genes subdivide the embryo into broad domains. Their (zygotic) expression
is regulated by maternal gene products, like Bicoid. In addition, gap
genes regulate each other, leading to a refinement of their expression
patterns. Gap genes
|
Gene
|
Type -
Domains
|
Function
|
Links
|
|
buttonhead
(btd)
|
transcription
factor - zinc finger
|
transcriptonal
activator that regulates the segmentation of the head
|
|
| cap'n'collar (cnc) | transcription factor - basic leucine zipper | involved in the segmentation of the head - effects both labral and mandibular structures | Interactive Fly |
|
caudal
(cad)
|
transcription
factor - homeodomain
|
plays a role in establishing the posterior domains
of the embryo
|
|
| collier (col)
(preferred name: knot (kn)) |
EBF/Olf-1 homolog, HLH protein | required for the formation
of the hypopharyngeal lobe, the proper development of the larval head skeleton, and suppresses vein formation between veins 3 and 4 |
Interactive Fly |
|
crocodile (croc)
|
transcription factor - winged helix, forkhead
family
|
establishing the domains of expression for wingless
and engrailed in the clypeolabrum,
the anterior most segment of the fly's head |
|
|
empty
spiracles (ems)
|
transcription
factor - homeodomain
|
required for head + brain development
|
|
|
giant (gt)
|
transcription factor - basic leucine zipper
|
gap gene
|
|
|
huckebein (hkb)
|
transcription factor - zinc finger
|
gap gene (terminal) limits the extent of mesodermal
development - required for proper endoderm formation
|
|
|
hunchback
(hb)
|
transcription factor - zinc finger |
gap gene, later required for proper temporal generation
of NB sublineages
|
|
|
knirps (kni)
|
transcription factor - steroid receptor - zinc
finger
|
gap gene, later organizes the development of the second
wing vein
|
|
|
Krüppel (Kr)
|
transcription factor - zinc finger transcriptional
repressor
|
gap gene, later required for proper temporal generation
of NB sublineages
|
|
|
orthodenticle
(otd)
|
transcription
factor - homeodomain - paired-like
|
acts in a combinatorial fashion with the cephalic gap
genes empty spiracles and buttonhead to
assign segmental identities in the head and brain
|
|
| sloppy paired 1 and sloppy paired 2 (Slp 1, Slp 2) | transcription factor - forkhead domain | has combined characteristics of a gap, pair rule and segment polarity gene | Interactive Fly |
|
tailless (tll)
|
transcription factor - nuclear receptor - zinc
finger
|
early and transient expression at the posterior pole
is required to establish the eighth abdominal segment, telson
and posterior gut
|