 The
gonads develop from cells of two different origins; the cells of the germline
(primordial germ cells) derive from the so-called pole
cells, whereas the somatic cells originate from the mesodermal
layer of abdominal segments a5, a6 and a7.
The
gonads develop from cells of two different origins; the cells of the germline
(primordial germ cells) derive from the so-called pole
cells, whereas the somatic cells originate from the mesodermal
layer of abdominal segments a5, a6 and a7.  The
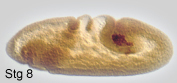
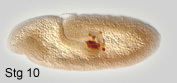
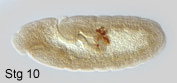
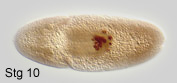
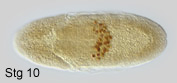
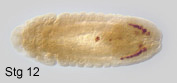
primordial germ cells or pole cells, are set aside very early in development.
They bud off at the posterior pole of the syncytial embryo. During embryonic
development, they are internalized with the midgut, migrate through the
midgut epithelium and along its basal surface, into the lateral trunk
mesoderm, where they will contact somatic gonad precursors of mesodermal
origin. During their extensive migration, a substantial number of pole
cells get lost. After completion of germ band shortening, the embryonic
gonads are visible as two dorsolateral cell clusters at the level of a5.
The
primordial germ cells or pole cells, are set aside very early in development.
They bud off at the posterior pole of the syncytial embryo. During embryonic
development, they are internalized with the midgut, migrate through the
midgut epithelium and along its basal surface, into the lateral trunk
mesoderm, where they will contact somatic gonad precursors of mesodermal
origin. During their extensive migration, a substantial number of pole
cells get lost. After completion of germ band shortening, the embryonic
gonads are visible as two dorsolateral cell clusters at the level of a5.
|
Lateral view
|
Dorsal view
|
|
      |
      |
|
Media list